Nervous System Overview: Understanding CNS and PNS Functions
The nervous system is a complicated network that regulates the body’s operations. In this Nervous System Overview, we’ll look at the two main components: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), and how they operate together to regulate critical bodily activities.
Functions of Brain
The brain is responsible for sensory input interpretation, muscle movement control, body temperature regulation, and higher cognitive activities such as memory, thinking, and decision-making.
Functions of Spinal Cord
The spinal cord serves as an important communication channel between the brain and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). It sends messages to control reflexes and movement. Damage to the spinal cord can significantly impair body control and nervous function.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Functions
The Peripheral Nervous System refers to all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Its primary job is to connect the CNS to the body’s limbs and organs, ensuring that brain signals reach muscles, skin, and internal organs. The PNS is organized into two main subsystems: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system regulates voluntary motions like walking and grasping objects by transmitting signals from the brain to the muscles. It also controls reflex actions, such as retreating from a hot surface.
Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary actions like heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It has two major branches:
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Activates the “fight or flight” response. This system prepares the body for stressful situations by increasing heart rate, dilating airways, and redirecting blood to muscles.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Promotes the “rest and digest” state. It helps the body relax, slows heart rate, stimulates digestion, and conserves energy during periods of rest.

Credit- https://copbela.org/
Summary of Nervous System Overview
In summary, the human nervous system has two major branches: the Central Nervous System (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body. The somatic nervous system regulates deliberate movements, whereas the autonomic nervous system governs involuntary actions. The autonomic system is further divided into two systems: sympathetic and parasympathetic, which govern stress and relaxation responses, respectively.

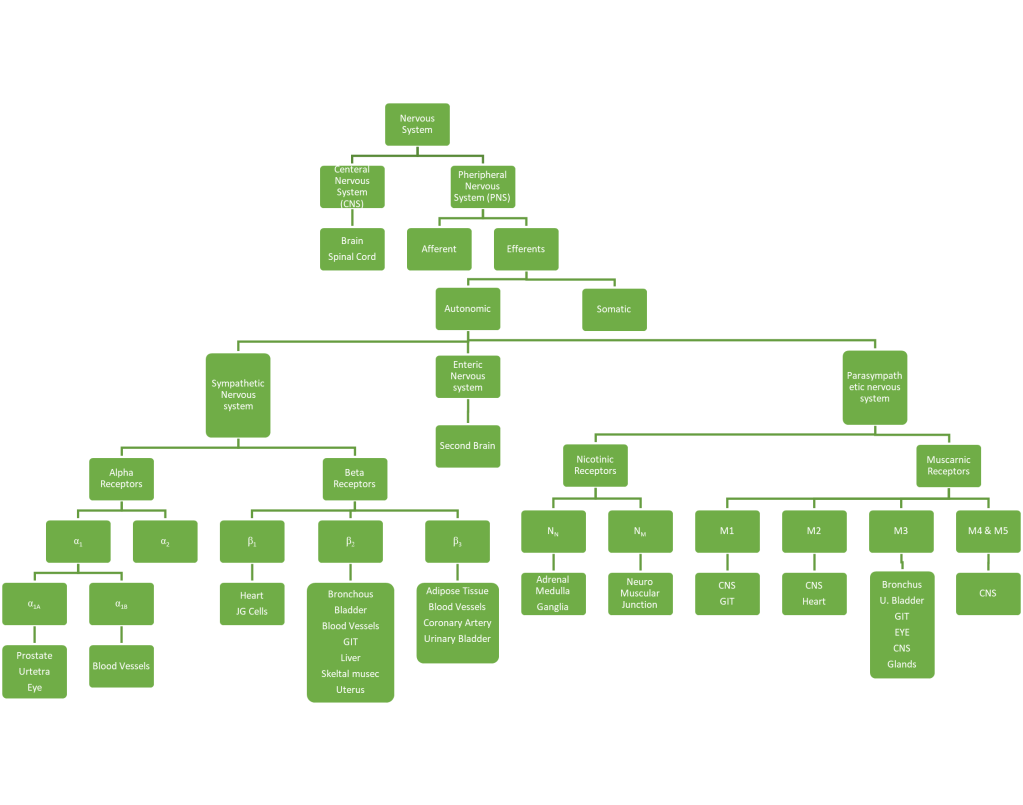
“This flowchart illustrates the detailed classification of the human nervous system, outlining its major components: the central nervous system (CNS), peripheral nervous system (PNS), somatic system, autonomic system, and further subdivisions including sympathetic and parasympathetic branches.”
🧬 Common Receptors, Substrates and Drug Examples 💊
Receptor | Endogenous Substrate | Agonist Action | Drug Agonists | Antagonist Action | Drug Antagonists |
Muscarinic | Acetylcholine | ↑ SLUDD | Pilocarpine, Bethanechol | ↓ SLUDD | Atropine Oxybutynin |
Nicotinic | Acetylcholine | ↑ HR, BP | Nicotine | Neuromuscular blockade | Neuromuscular blockers (e.g., Rocuronium) |
Alpha-1 | Epinephrine, Norepinephrine | Smooth muscle vasoconstriction, ↑ BP | Phenylephrine, Dopamine (dose-dependent) | Smooth muscle vasodilation, ↓ BP | Alpha-1 blockers (e.g., Doxazosin, Carvedilol, Phentolamine) |
Alpha-2 | Epinephrine, Norepinephrine | ↓ Release of epinephrine, norepinephrine, ↓ BP, HR | Clonidine, Brimonidine | ↑ BP, HR | Ergot alkaloids, Yohimbine |
Beta-1 | Epinephrine, Norepinephrine | ↑ Myocardial contractility, CO, HR | Dobutamine, Isoproterenol | ↓ CO, HR | Beta-1 blockers (e.g., Metoprolol, Propranolol, Carvedilol) |
Beta-2 | Epinephrine | Bronchodilation | Albuterol, Terbutaline, Isoproterenol | Bronchoconstriction | Non-selective beta-blockers (e.g., Propranolol, Carvedilol) |
Dopamine | Dopamine | Renal, cardiac, CNS effects | Levodopa, Pramipexole | Many effects on renal, cardiac, CNS | First-gen antipsychotics (e.g., Haloperidol), Metoclopramide |
Serotonin | Serotonin | Platelet, GI, psychiatric effects | Triptans (e.g., Sumatriptan) | Many effects on platelet, GI, psychiatric | Ondansetron, Second-gen antipsychotics (e.g., Quetiapine) |

Leave a Reply