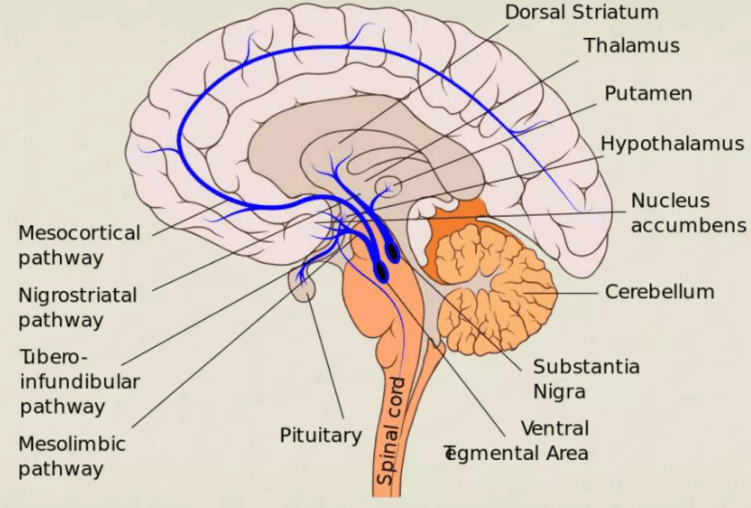
The mechanism behind EPS primarily involves the blockade of dopamine D2 receptors in the nigrostriatal pathway. This case report emphasizes the need for awareness of this risk when prescribing antipsychotic medications.” …
Risperidone Induced Extrapyramidal Side Effects
By
hemanthbesabathini@gmail.com
Research & Publications
Akathisia, Antipsychotic-induced akathisia, Antipsychotics and involuntary movements, Dopamine antagonism and EPS, Dopamine receptor blockade, EPS symptoms in psychiatric treatment, Extrapyramidal symptoms, Managing EPS in antipsychotic therapy, Managing side effects of antipsychotics, Nigrostriatal pathway dopamine antagonism, Parkinsonism and antipsychotics, Pseudoparkinsonism, Risperidone and motor control disorders, risperidone contraindications, risperidone contraindications/precautions, Risperidone dosage adjustments, Risperidone EPS case report, risperidone mechanism of action, Risperidone side effects, Risperidone-induced extrapyramidal side effects (EPS), Schizophrenia treatment and EPS, Second-generation antipsychotics